APPLIANCES AND EQUIPMENT
LED Lamps
What are LEDs?
Lighting Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are solid-state semiconductor devices that convert electrical energy into visible light. The semi-conductor LED chip is supported by a reflector and encapsulated with an epoxy lens for controlling light distribution. When direct circuit (DC) voltage is applied, the electrons flowing through the chip will cause emission of electromagnetic wave (light) at certain frequency (colour). Emitting monochromatic visible light of different colour is made possible by selecting different semiconductor materials.
What are the major components of LED lamp?
LED lamp is made up of the following major components:
- Light source: LEDs, in a package, or mounted on a circuit board;
- Optics: Phosphors in silicone gel, or, in a plastic lens, micro-structure lenses for beam pattern control and reflectors;
- Electrical/ electronic components: circuit board; AC or DC transformer; circuit driver; feedback loops and sensors; on/ off/ dimming control; and
- Mechanical and thermal components: conductive adhesive and heat sink.
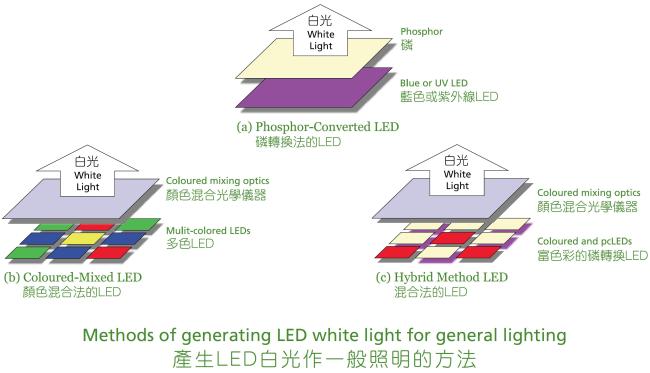
How is white light made with LEDs?
LEDs emit light in small band of wavelengths, producing coloured light. LEDs use following methods to create white light for general lighting purpose:
- Colour mixing - Uses three individual LED chips (red, green and blue) each emitting a different wavelength in close proximity, to form the broad white light spectrum;
- Phosphor conversion - Uses blue or ultra-violet LED to combine with phosphor;
- Hybrid - combine phosphor conversion and colour mixing approach.
The colour mixing approach can achieve the highest efficacy white lights although the light is more sensitive to colour shift arising from temperature and aging. Whereas, the phosphor conversion approach will produce white light with good colour rendering index (CRI) and high efficacy. Currently, most LEDs adopt phosphor conversion approach to produce white light because of lower production cost and good CRI for general lighting purpose.
Luminous Efficacy
The luminous efficacy of LED is ranges from 65 to 110 lm/W. It is more energy efficient than incandescent bulb, compact fluorescent lamp and tungsten halogen lamp. When compared with T5 fluorescent tubes and high intensity discharge lamp, LED is comparable to them. However, as the rapid technological advances in solid-state lighting system, the luminaries efficacy of LED lamp is increasing rapidly and the trend is expected to continue. It is expected that within the next few years LED lighting will surpass the efficiency of any other lightings.
Comparison of efficacy of different lamps:
http://www.energyland.emsd.gov.hk/en/appAndEquip/equipment/lighting/tubes.html
Advantages of using LED
- Long-life – Some high quality LED luminaries that work properly within its temperature limit will last about 25,000 to 50,000 hours, which is about 3 to 6 times as long as compact fluorescent lamps, and far longer than typical incandescent lamp with service life of about 1,000 hours.
- Robust and reliable – LEDs having no filament to break are inherently rugged. They are also difficult to damage with external shock, unlike fluorescent lamp and incandescent bulbs, which are fragile.
- Versatile colour changes – LEDs response quickly to both switching and dimming and It is very suitable for dynamic lighting effect.
LED lighting applications in Government Buildings
The government has installed LED lightings in some government buildings such as general lighting at corridors, canteens, conference rooms, classrooms, assembly halls, parks, swimming pools, fountains, etc.



