ENERGY AUDIT AND CARBON AUDIT
Energy Audits
What is Energy Audit?
Energy audit is a regular review of the usage of energy in a building to increase effectiveness of energy. The auditors examines the energy account of energy consuming equipment, checks the way energy is used in its various components and identifies savings opportunities. An energy audit process typically includes:
- Analysis and assessment of your system/equipment's energy performance
- Identification of "Energy Management Opportunities (EMOs)"
- Potential saving estimates
- Recommendations for energy savings solutions.
Benefits from Energy Audit
Energy Audit is an effective energy management tool. By identifying and implementing the means to achieve energy efficiency and conservation, not only can energy savings be achieved, but also equipment/system services life can be extended. All these mean savings in money. Based on the principle of "The less energy is consumed, the less fossil fuels will be burnt", the power supply companies will generate relatively less pollutants and by-products. Therefore, all parties concerned contribute to conserve the environment and to enhance sustainable development

Typical Procedure to Conduct Energy Audit
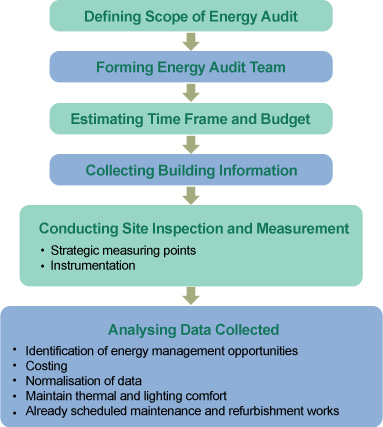
- Defining scope of energy audit, e.g. walk through audit is suitable for organization with limited resource and detailed audit is suitable for organization with more resources
- Forming an energy audit team. The team shall include management representatives, maintenance professionals & staff representatives etc.
- Estimate time frame & budget, e.g. auditor-hours, whether any disruption to the occupants, and the cost of measuring instruments etc.
- Collecting building information, e.g. floor area, building orientation, equipment design condition, energy bills and system schematic diagrams etc.
- Conducting site inspection & measurement to identify means for improvement
- Analysing data collected
- Recommending the improvement actions and measures
Flow Chart on Conducting Energy Audit
Energy audit report
The report should outline the objectives and scope of audit, description of characteristics and operational conditions of equipment/systems audited, findings in the audit, EMOs identified, corresponding savings and implementing costs, recommendations on EMO implementation and programme and any other follow-up actions.
Upon completion of all EMOs identified in an energy audit, a minimum energy saving of 5%-10% could be achieved for a typical commercial building.
For more information, please refer to EMSD's "Codes & Technical Guidelines" on energy audit for buildings.
Carbon audit
What is a carbon audit?
A carbon audit, sometimes referred to as a 'carbon footprint', is a means of measuring and recording the GHG emissions of an organization or building within a defined system boundary.
Carbon audit in Hong Kong
Climate change is one of the most important challenges facing mankind. Government is embarking upon a series of measures to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. These include promoting use of cleaner energy and renewable energy, improving energy efficiency and energy conservation, encouraging greening and raising public awareness.
Being a service economy without any major energy-intensive industries, electricity generation is the major source of GHG emissions in Hong Kong, accounting for over 60% of the total local emissions. The transport sector is the second largest GHG emission source (16%), followed by waste (12%). Among various end uses of electricity, buildings account for some 89% in Hong Kong.
To reduce GHG emissions arising from electricity consumption in buildings, it is believed that an important step which could be taken by owners and managers of buildings is to find out the amount of GHG released to the atmosphere arising from the operation of their buildings and to take appropriate actions to reduce such emissions.
To facilitate carbon audit action, the Environmental Protection Department (EPD) and the Electrical and Mechanical Services Department (EMSD) have drawn up a set of "Guidelines to Account for and Report on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Removals for Buildings in Hong Kong". The Guidelines provide a systematic and scientific approach for building owners and managers to account for and report on the GHG emissions arising from the operations of their buildings in Hong Kong, identify areas of improvement and conduct voluntary programmes to reduce and / or offset emissions arising from buildings according to the their own goals. For detail information of carbon audit, please visit https://cnsd.gov.hk/en/green-business-and-industry/carbon-audit/