-
1.Why does a failure of power supply system not affect safety?
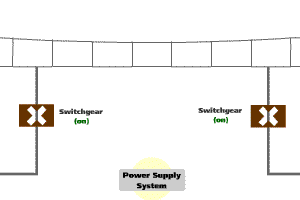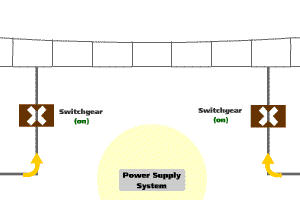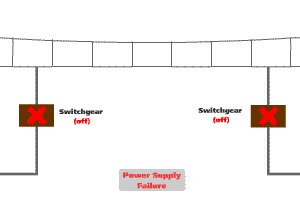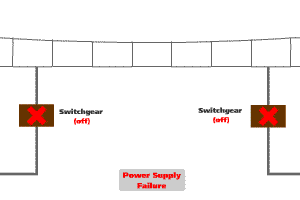
The power supply system is designed and operated under the "fail-safe" principle. The "fail-safe" feature ensures that, in the event of a fault of power supply equipment, the system will be de-energised so that it will cause no harm to other devices or danger to personnel. Under the circumstance that the failure causes the loss of train power supply, the emergency lighting and ventilation fans within the train will continue to operate with power supplying from the standby batteries of the train.
-
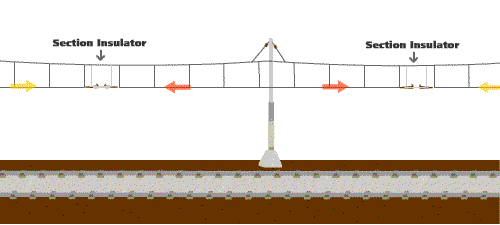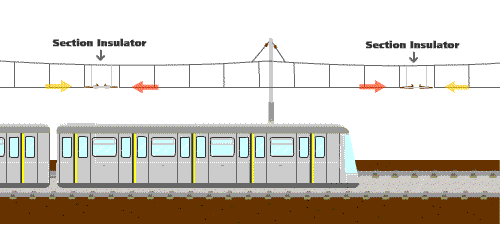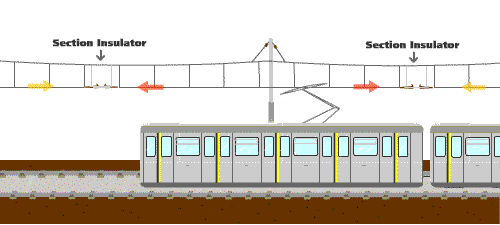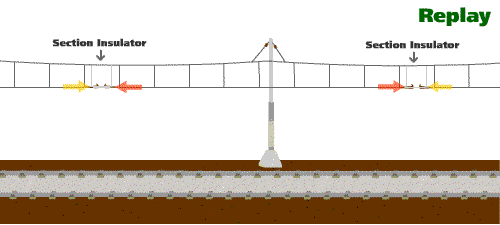
2.Why is a flash sometimes observed at the overhead line when a train is running?
At certain locations along the overhead line system, equipment known as "section insulators" are installed to segregate the different power supply zones. It is common that there may be slight electrical potential difference between two power supply zones. Thus, when a pantograph of a train is traversing across a section insulator, it will bridge the two different power supply zones that may be at different electrical potentials and result in a flash at the overhead line. This kind of flash is normal and will not hamper railway safety.