ENERGY
Global warming
Energy from the sun drives the Earth weather and climate, and heats up the Earth's surface. In turn, the Earth radiates energy back into space. Atmospheric greenhouse gases, in particular carbon dioxide CO2, trap some of the outgoing energy, retaining heat somewhat like the glass panels of a greenhouse. Earth’s surface temperature rose by 0.56 to 0.92 °C over the period 1906 – 2005.
Causes of global warming
The increasing concentrations of anthropogenic greenhouse gases, which result from human activities, account for the temperature increase of the Earth since the mid 20th century. The main source of anthropogenic greenhouse gases is the burning of fossil fuel (coal, oil, and natural gas) which occurs in power plants, transportation and industrial processes. Deforestation also indirectly contributes to the buildup of CO2 in the atmosphere by reducing CO 2 absorbed in plants’ photosynthesis.
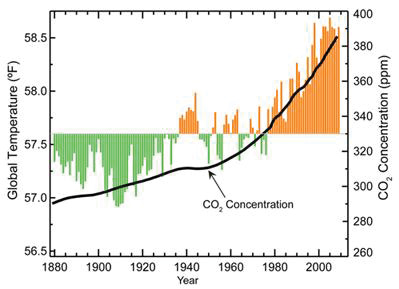
The impact of global warming
Continued global warming could bring a series of damaging effects. Global warming could mean polar ice melting to raise the sea level. Global average sea level rose at an average rate of 1.8 mm per year over 1961 to 2003 and at an average rate of about 3.1 mm per year from 1993 to 2003. Global warming also damages the ecosystems of plants and animals. As a result of habitat loss, animals may be forced to migrate to other habitats. It is assessed that about 20 to 30% of plant and animal species are exposed at increased risk of extinction if global average temperature increases more than 1.5°C. It could change the normal weather patterns and cause drought, flooding and other extreme weather conditions.
Limiting global warming
Many countries are now pursing a broad range of strategies to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases from both the energy supply and demand aspects.
For the supply side, greenhouse gas emission can be reduced through the development of cleaner, more efficient technologies for electricity generation and transmission. Besides, more governments are supporting the development of renewable energy, such as solar energy, wind power, hydropower, bio-energy and hydrogen.
For the demand side, various kinds of energy efficient technologies, such as heat recovery in air-conditioning systems and high efficient lighting systems, have been developed and widely used. People also have growing awareness in energy conservation, such as switching off lighting and equipment in unoccupied space, adjusting air-conditioning set point temperature to avoid over cooling, adopting sensors to reduce unnecessary operation of various equipment and appliances etc.
In addition, many countries are promoting the use of fuel-efficient motor vehicles and trucks, researching cleaner fuels and alternative fuel vehicles, and implementing programmes to reduce vehicle use.