ENERGY
Wind Energy
What is wind?
Wind is the movement of air mass as a result of variations in air pressure, which is produced by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. Since the Earth’s surface is made of different types of land and water, it absorbs the sun’s radiant energy at different rates. Much of this energy is converted into heat as it is absorbed by land areas, bodies of water, and the air over these formations.
Wind is called a renewable energy source because wind will continually be produced as long as the sun shines on the Earth. Today, wind energy is mainly used to generate electricity.
How does wind turbine work?
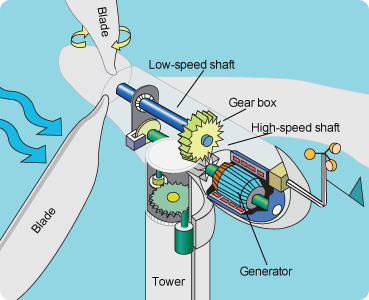
Today, wind is harnessed and converted into electricity using machines called wind turbines. The amount of electricity that a turbine produces depends on its size and speed of the wind. All wind turbines have the same basic parts: blades, a tower, and a gearbox. These parts work together to convert the wind’s kinetic energy into mechanical energy that generates electricity.
- The moving air spins the turbine blades.
- The blades are connected to a low-speed shaft. When the blades spin, the shaft turns.
- The low-speed shaft is connected to a gearbox. Inside, a large slow-moving gear turns a small gear quickly.
- The small gear turns another shaft at high speed.
- The high-speed shaft is connected to a generator. As the shaft turns the generator, it produces electricity.
- The electric current is sent through cables down the turbine tower to a transformer that changes the voltage of the current before it is sent out on transmission lines.
How much energy can we get from the wind?
There are two terms to describe basic electricity production: efficiency and capacity factor. Efficiency refers to how much useful energy (electricity, in this case) we can get from an energy source.
How efficient are wind machines? Wind machines are just as efficient as most other plants, such as coal plants. Wind machines convert 30-40 percent of the wind’s kinetic energy into electricity. A coal-fired power plant converts about 30-35 percent of the chemical energy in coal into usable electricity.
Capacity refers to the capability of a power plant to produce electricity. A wind turbine at a typical wind farm operates 65-80 percent of the time, but usually below its full capacity, because the wind speed is not always at optimum levels. Therefore, its capacity factor is 30-35 percent.

